Swaps data: cleared vs non-cleared margin
Growing margin burden for non-cleared swaps means cleared margin is likely to grow further, argues Amir Khwaja
Initial margin numbers are growing for the over-the-counter derivatives market – a result of rules that require some products to be centrally cleared, as well as separate requirements compelling a growing band of firms to collect margin for non-cleared trades.
But the two regulatory edifices function in different ways and also interact, it is likely that, as the non-cleared rules steadily expand, they will encourage more firms to clear voluntarily and create incentives for the scope of cleared products to be widened as well.
Currently, the non-cleared margining regime requires approximately 50 financial groups to collect and post initial margin for OTC derivatives they trade bilaterally. The first phase of 20 firms started doing so on September 1, 2016 and only for new trades executed subsequent to that date, so it will have taken some time to build up to the $50 million exposure threshold above which initial margin must be collected and posted.
The remaining phases in September 2019 and September 2020, cover phase four and phase five firms with – respectively – greater than $750 billion and $8 billion of gross notional in non-cleared derivatives. The influx of new firms has been estimated at 1,100 in a recent document by the International Swaps and Derivatives Association, the Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association and other trade associations.
Given the size of the numbers involved, let’s look at the data on initial margin.
Initial margin for non-cleared derivatives
Isda’s most recent annual margin survey was published in April this year, covering 2017. It provides interesting insights as it has data provided by the 20 largest market participants (phase one firms).
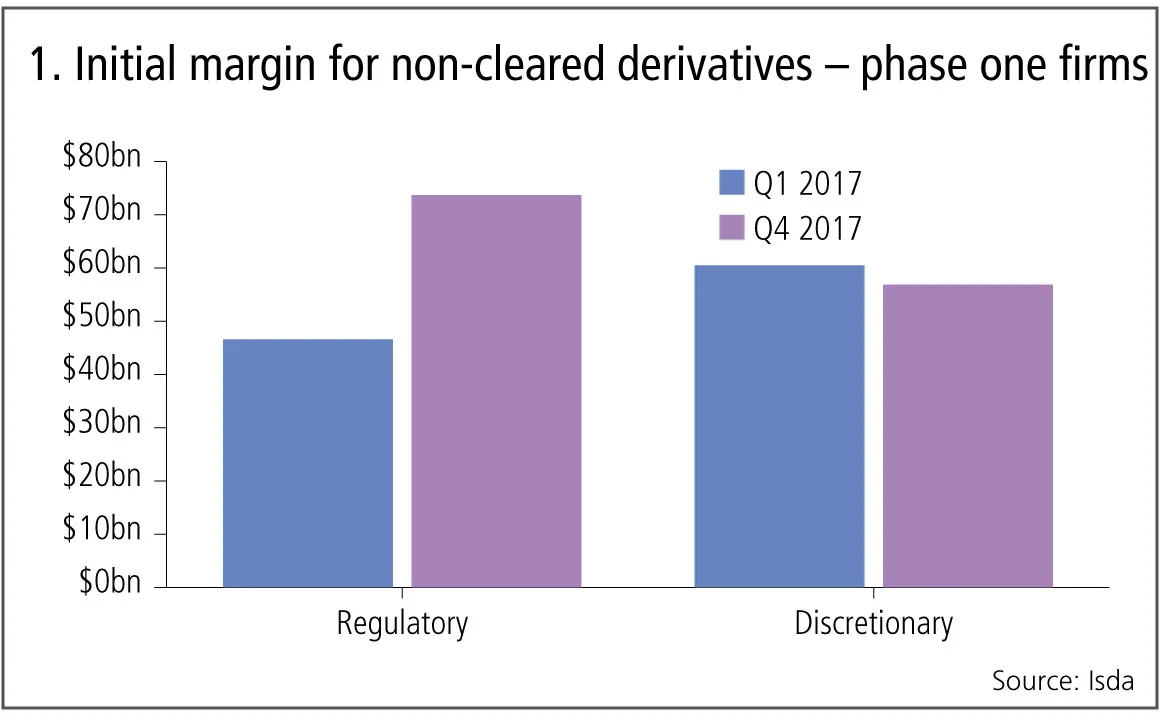
Figure 1 shows:
- Regulatory initial margin increasing from $46.6 billion at the end of Q1 2017 to $73.7 billion at the end of Q4 2017, an increase of 58%.
- Isda attributes the large increase to the fact that each month more and more new trades are executed and so fall under the initial margin rules.
- In addition a smaller number of phase two firms started complying with the rules on September 1, 2017.
- Discretionary initial margin decreased to $56.9 billion from $60.5 billion, a drop of 6%.
- Isda attributes this decrease to more firms falling into regulatory initial margin, so more and more of this will move into the regulatory bucket.
A cumulative $131 billion of initial margin as at end Q4 2017 sounds like a large amount indeed, let’s see how this compared to cleared OTC derivatives.
Initial margin for cleared OTC derivatives
Disclosures required of central counterparties (CCPs) by the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures and the International Organization of Securities Commissions cover initial margin totals. Using the data we can aggregate seven of the largest OTC derivative clearing services: CME IRS, Eurex OTC IRS, Ice Credit Clear, Ice EU CDS, JSCC IRS, LCH ForexClear and LCH SwapClear.
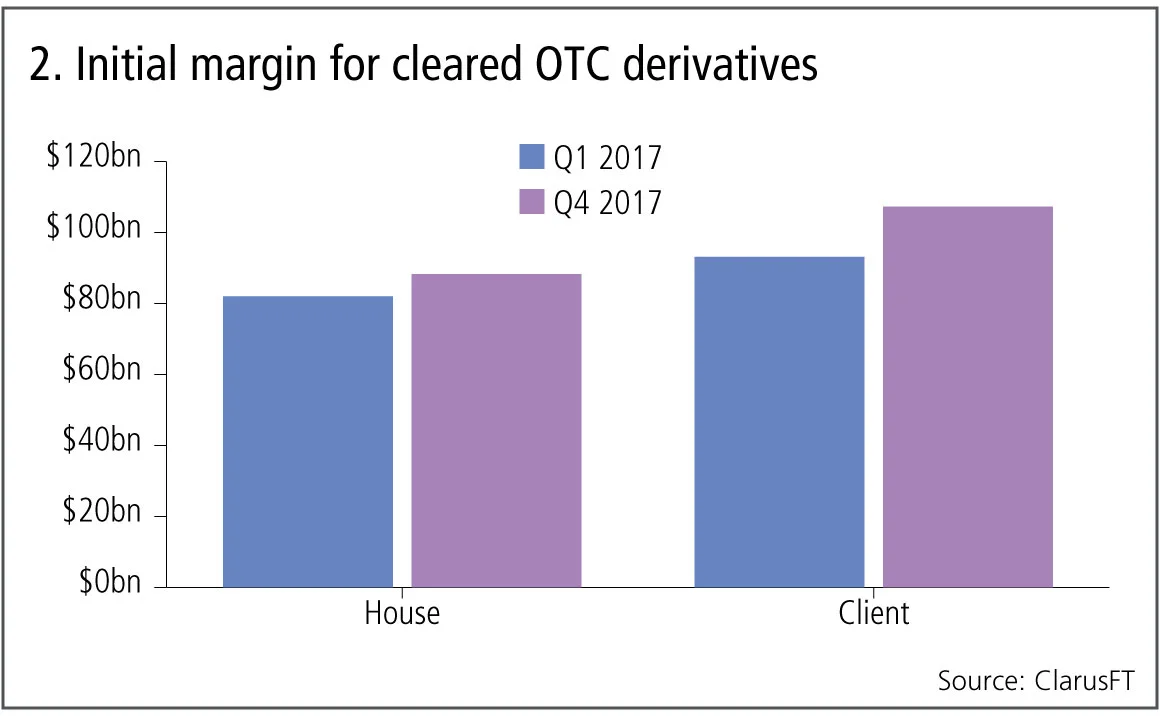
Figure 2 shows:
- House (or member) initial margin increasing from $82 billion to $88.3 billion over the same period, an increase of 8%.
- Client initial margin increasing from $93 billion to $107 billion from Q1 2017 to Q4 2017, an increase of 15%.
- A cumulative total of $196 billion of initial margin at end Q4 2017, so significantly larger than the $131 billion of cumulative uncleared initial margin in the prior section.
- It is also interesting to note the ratio of house to client initial margin is 45% to 55%, so while house margin contains the largest market participants – which are also the phase one, two and three firms in the non-cleared regime – the fact that client initial margin is larger is a reflection of the fact that these portfolios are more directional and so attract larger initial margin.
Now, in comparing cleared initial margin and uncleared initial margin, we have to be cognisant of the differences; in particular, in how netting operates.
Multilateral netting
One of the most important benefits of central clearing is multilateral netting, meaning all my exposures can be netted down to one margin number, as opposed to individual bilateral margins against each counterpart. While this is of great benefit for variation margin, it is even more important for initial margin as the following figure illustrates.
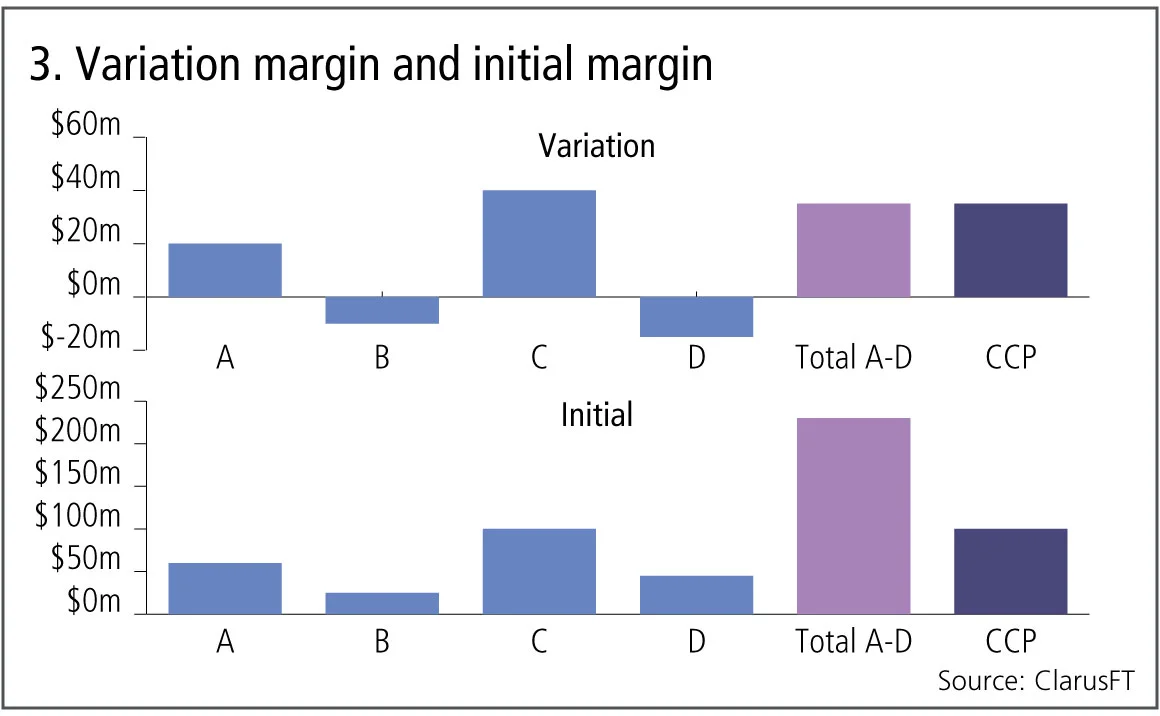
Figure 3 shows:
- Variation margin that needs to be paid or received on a given day to each of four counterparties; A to D, the total of these is $35 million.
- If these same position were all cleared at one CCP, the net variation margin payment would also be $35 million, so economically exactly the same.
- However for IM, the situation is very different, as the sum of the four bilateral IM amounts is $230 million, while if one CCP cleared all of these, the IM could be $100 million, so economically the market is much better off.
In reality, market participants cannot net all cleared OTC derivatives into one CCP, so does the illustrated multilateral example still hold?
The answer is yes, as while a market participant may use a handful of CCPs for OTC derivatives, generally less than 10, the same participant is likely to have bilateral derivatives exposures against a much larger number of counterparties, generally in the low hundreds.
Consequently, the grossing up of initial margin in each of those relationships as more and more firms are captured by uncleared margin rules is likely to increase regulatory initial margin more and more.
The $50 million threshold below which initial margin only needs to be calculated and not collected and posted helps mitigate matters, however we still expect to see uncleared margin rules act as an incentive for firms to clear.
Increasing clearing
This incentive to clear, as well as mandatory clearing of certain products should mean cleared initial margin for OTC derivatives will continue growing for some years yet.
Let’s see if more recent data bears that out.
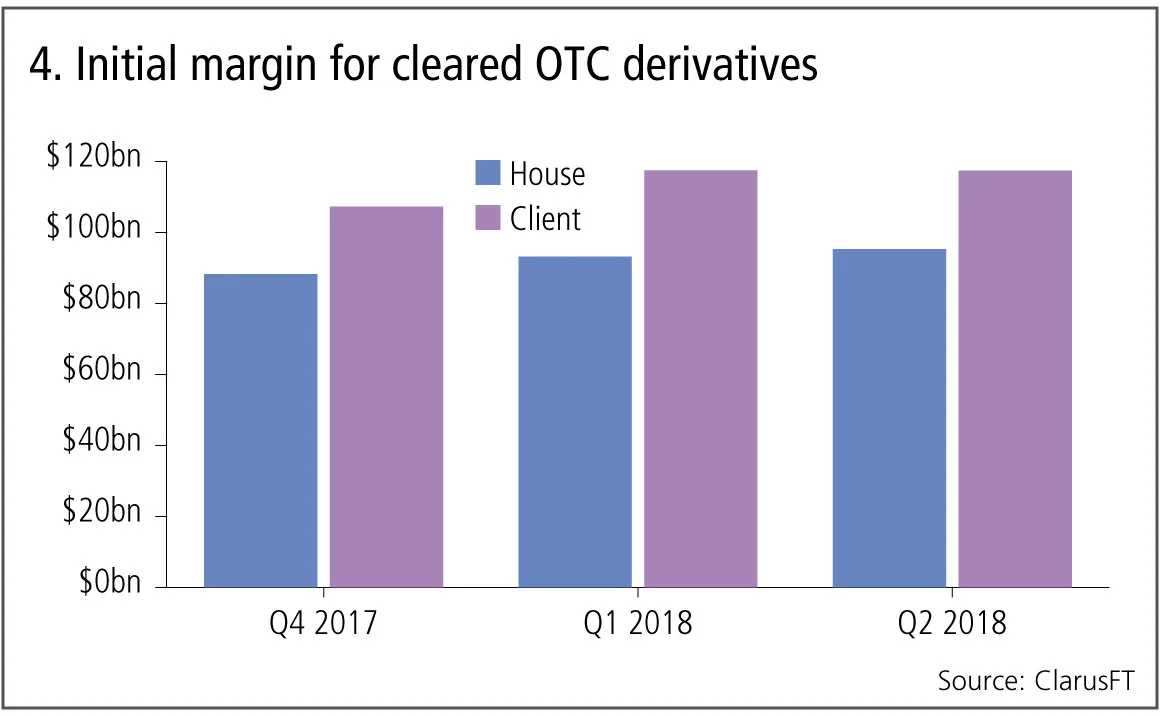
Figure 4 shows:
- House initial margin increasing from $88.3 billion at Q4 2017 to $95.3 billion at Q2 2018.
- Client initial margin increasing from $107 billion to $117 billion.
- A total of $213 billion initial margin at Q2 2018, up 9% over the six-month period, which projecting at the same rate implies 18% annual growth rates.
Default resources
Before I end, it is worth mentioning CCPs also require their members to contribute to a defult fund. Below, we aggregate default resources for the same OTC CCPs, excluding Eurex, which has a combined default fund.
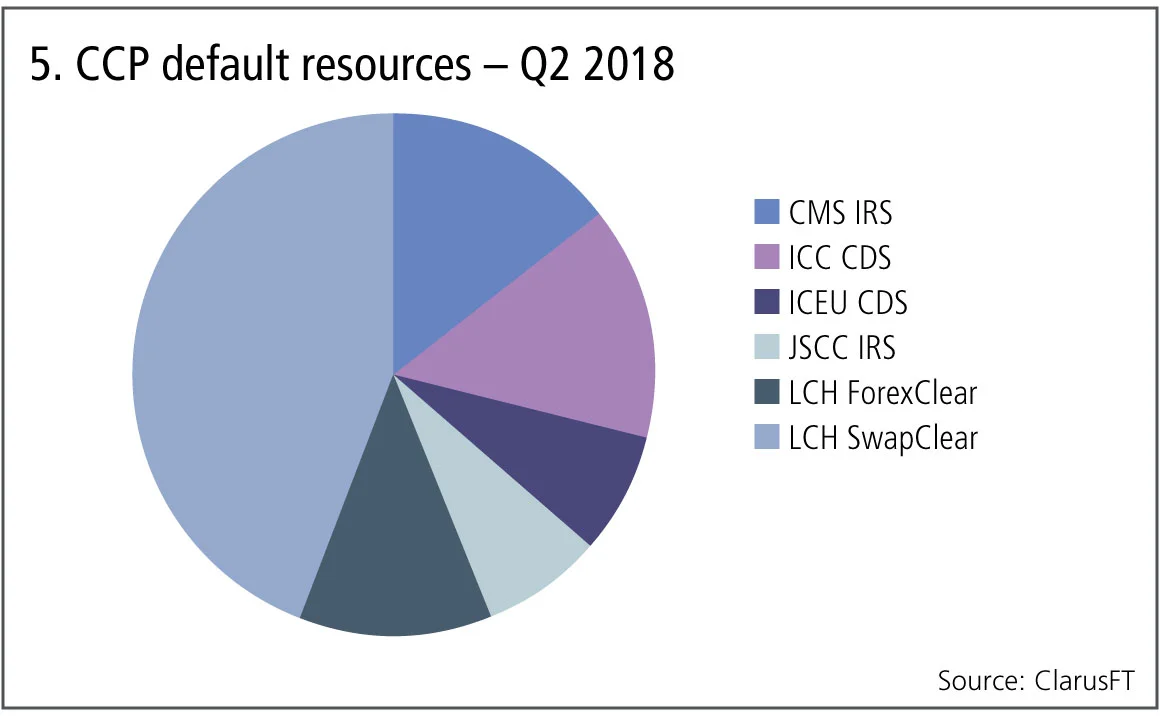
Figure 5 shows:
- Composition of the pre-funded and committed financial resources available to each of the CCPs.
- A cumulative $16 billion of prefunded resources and a further $14 billion of resources that are committed on default of a member, a grand total of $30 billion.
This additional $30 billion provides additional security and a backstop to member defaults, above and beyond the $213 billion of initial margin held for cleared OTC derivatives.
Amir Khwaja is chief executive of Clarus Financial Technology.
コンテンツを印刷またはコピーできるのは、有料の購読契約を結んでいるユーザー、または法人購読契約の一員であるユーザーのみです。
これらのオプションやその他の購読特典を利用するには、info@risk.net にお問い合わせいただくか、こちらの購読オプションをご覧ください: http://subscriptions.risk.net/subscribe
現在、このコンテンツを印刷することはできません。詳しくはinfo@risk.netまでお問い合わせください。
現在、このコンテンツをコピーすることはできません。詳しくはinfo@risk.netまでお問い合わせください。
Copyright インフォプロ・デジタル・リミテッド.無断複写・転載を禁じます。
当社の利用規約、https://www.infopro-digital.com/terms-and-conditions/subscriptions/(ポイント2.4)に記載されているように、印刷は1部のみです。
追加の権利を購入したい場合は、info@risk.netまで電子メールでご連絡ください。
Copyright インフォプロ・デジタル・リミテッド.無断複写・転載を禁じます。
このコンテンツは、当社の記事ツールを使用して共有することができます。当社の利用規約、https://www.infopro-digital.com/terms-and-conditions/subscriptions/(第2.4項)に概説されているように、認定ユーザーは、個人的な使用のために資料のコピーを1部のみ作成することができます。また、2.5項の制限にも従わなければなりません。
追加権利の購入をご希望の場合は、info@risk.netまで電子メールでご連絡ください。
詳細はこちら コメント
大げさな宣伝を超えて、トークン化は基盤構造を改善することができる
デジタル専門家によれば、ブロックチェーン技術は流動性の低い資産に対して、より効率的で低コストな運用手段を提供します。
GenAIガバナンスにおけるモデル検証の再考
米国のモデルリスク責任者が、銀行が既存の監督基準を再調整する方法について概説します。
マルキールのサル:運用者の能力を測る、より優れたベンチマーク
iM Global Partnersのリュック・デュモンティエ氏とジョアン・セルファティ氏は、ある有名な実験が、株式選定者のパフォーマンスを評価する別の方法を示唆していると述べています。
IMAの現状:大きな期待と現実の対峙
最新のトレーディングブック規制は内部モデル手法を改定しましたが、大半の銀行は適用除外を選択しています。二人のリスク専門家がその理由を探ります。
地政学的リスクがどのようにシステム的なストレステストへと変化したのか
資源をめぐる争いは、時折発生するリスクプレミアムを超えた形で市場を再構築しています。
オペリスクデータ:FIS、ワールドペイとのシナジー効果の失敗の代償を支払うことに
また:ORXニュースによるデータで、リバティ・ミューチュアル、年齢差別訴訟で過去最高額を支払う;ネイションワイド、不正防止対策の不備。
東京の豊富なデータが市場への影響について明らかにすること
新たな研究により、定量金融において最も直感に反する概念の一つが普遍的であることが確認されました。
資金調達コストの配分:集中型 vs 分散型
サチン・ラナデ氏は、特に担保付融資において、集中化は資本効率と自己資本利益率(ROE)の向上に寄与し得ると述べています。