
Spread options, Farkas's lemma and linear programming
Vladimir Piterbarg derives necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of a joint distribution consistent with given marginals and the distribution of the spread in terms of no-arbitrage conditions among certain payouts. He also proposes a generic numerical approach to constructing such distributions, and identifying payouts that realise arbitrage if it exists
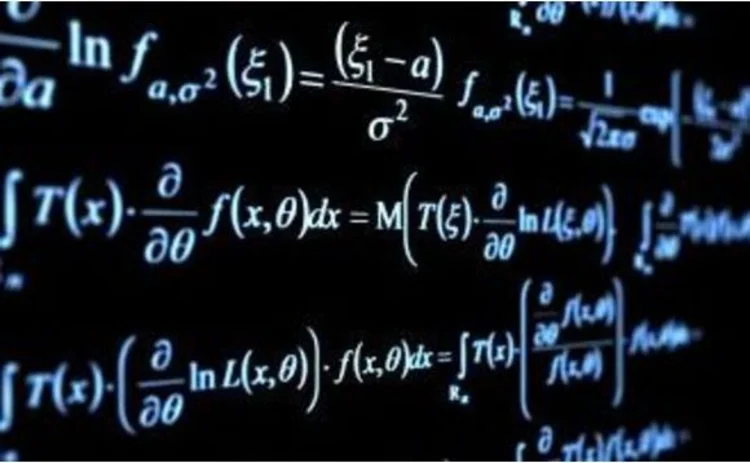
Options on individual underlyings are very liquid in a variety of markets. In many markets, moreover, options on linear combinations of underlyings are also reasonably liquid. Of primary interest to us are markets with liquid spread options (that is, options on the difference of two underlyings), such as constant maturity swap (CMS) spread options in interest rate markets. Our discussion also
Only users who have a paid subscription or are part of a corporate subscription are able to print or copy content.
To access these options, along with all other subscription benefits, please contact info@risk.net or view our subscription options here: http://subscriptions.risk.net/subscribe
You are currently unable to print this content. Please contact info@risk.net to find out more.
You are currently unable to copy this content. Please contact info@risk.net to find out more.
Copyright Infopro Digital Limited. All rights reserved.
As outlined in our terms and conditions, https://www.infopro-digital.com/terms-and-conditions/subscriptions/ (point 2.4), printing is limited to a single copy.
If you would like to purchase additional rights please email info@risk.net
Copyright Infopro Digital Limited. All rights reserved.
You may share this content using our article tools. As outlined in our terms and conditions, https://www.infopro-digital.com/terms-and-conditions/subscriptions/ (clause 2.4), an Authorised User may only make one copy of the materials for their own personal use. You must also comply with the restrictions in clause 2.5.
If you would like to purchase additional rights please email info@risk.net
More on Markets
BBVA joins growing Spire repack platform
Spanish bank becomes 19th dealer on multi-bank SPV issuer amid rising investor interest
ISITC’s Paul Fullam on the ‘anxiety’ over T+1 in Europe
Trade processing chair blames budget constraints, testing and unease over operational risk ahead of settlement move
Integration strengthens e-trading in persistently volatile markets
Survey reveals that traders are grappling with daily volatility, while technology outranks liquidity as the top market structure concern
How Optimal aims to shake up US retail options trading
New wholesaler has assembled a team of market-makers to compete with Citadel, IMC/Dash and Jane Street
Repo stress drove 2025 SOFR-to-fed funds swap pivot
SOFR OIS volumes slipped to almost half of fed funds activity during September repo spikes
Renminbi options volumes plummet as vol grinds lower
USD/CNH volumes fell 84% in 2025 as PBoC currency management took hold
Esma to issue guidance on active account reporting
Briefing and Q&A aims to clarify how firms should report data ahead of RTS adoption
Forex looks to flip the (stable)coin
Friction-free foreign exchange is the prize offered by stablecoins such as Tether and USDC. But the prize remains elusive








